Computer based information system developed in the framework of the project
"RADARM" requires use of IBM or compatible personal computer with
processor 486 or hihger, 16 MB RAM and volume of hard disk at
least 500 MB.
Information of radioecological character is recorded in the memory
of computer as numerical maps of various scales and electronic
data bases (in the form of tables). The volumes of accumulated
information are as follows:
Building of electronic maps showing required radioecological and other data (levels of radioactive contamination, spatial distribution of radionuclides and their migration, doses of people irradiation etc.) is realized by specially developed program with shell adopted for Windows(3.1, 3.11, 95).
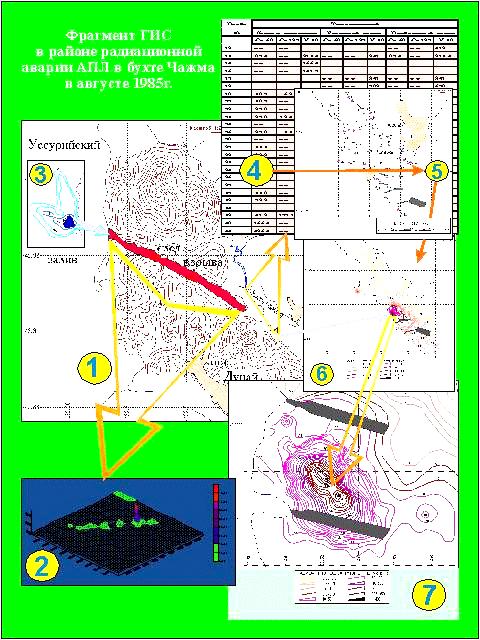
As an example at the end of this page the picture containing several
fragments of geoinformation
system (including electronic maps and tables) demonstrating radiation
situation in
the Chazhma bay (Primorski krai, Far East) and surroundings is shown. It is
the place of nculear accident on atomic submarine of Pacific Fleet.
Let us emphasize that this information is presented at first time
in our data base. Central place on the picture (fragment 1) is
occupied by map showing the position of the trace of fallouts from
radioactive cloud crossed Dunai peninsula. Fragment 2 shows levels
of gamma radioactivity along the trace, fragment 3 - radioactive
contamination of bottom sediments by cobalt-60 radionuclide in the
point of exit of radioactive trace on the aquatorie of Ussuri Bay.
Fragment 4 is a tipical electronic table containing data base
on radioactive contamination of bottom sediments directlyin the bay
Chazhma close to points shown on fragmet 5. Fragments 6 and 7 reflects
levels of radioactive contamination for all bay area and close to
the point of accident near the moorages.
Developed GIS supports the following options:
